- Details
- Written by: Germán Fernández
- Category: The chemical industry
- Hits: 285

Solvay (Torrelavega)
Some definitions of chemical engineering:
Chemical engineering is the profession in which knowledge of mathematics, chemistry, and other natural sciences, acquired through study, is applied judiciously to develop economical ways for the use of materials and energy for the benefit of humanity." (A.I.Ch.E.)
"Chemical engineering is the art of conceiving, calculating, designing, having built, and operating facilities where any chemical transformation can be carried out on an industrial scale." (Prof J. Cathalá)
"Chemical engineering is knowing how to do chemistry on an industrial scale." (Prof. A. Vian)
"Chemical engineering is a branch of engineering related to processes in which substances undergo a change in their composition, energy content, or physical state." (The Institution of Chemical Engineers of Great Britain)
- Details
- Written by: Germán Fernández
- Category: The chemical industry
- Hits: 267
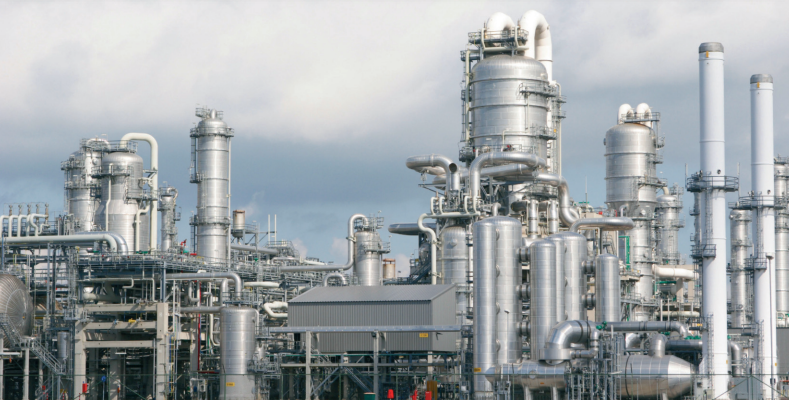

A chemical process is a set of chemical and/or physical operations aimed at transforming initial materials into different final products.
It is a sequence of steps or operations carried out with the purpose of transforming one or more chemical substances into one or several different substances. These processes may involve a variety of activities, such as mixing, heating, cooling, separating, reacting, purifying, and manipulating chemical substances to obtain desired products. Chemical processes are fundamental in the chemical, pharmaceutical, petrochemical, food, and various other industries, and are used for the production of a wide range of chemicals, materials, and end products. These processes are often carried out following specific protocols and procedures with the aim of safely and efficiently obtaining chemicals with desired properties.
- Details
- Written by: Germán Fernández
- Category: The chemical industry
- Hits: 326

Chemicals can be classified into five groups:
Basic Products: These are products consumed in large quantities, with little value per unit of mass, obtained by the basic industry from natural sources. These basic products are used to produce a large number of more elaborate products.
Basic chemical products are substances considered fundamental in chemistry and industry due to their importance in obtaining other compounds or more complex chemical products. These basic chemical products often serve as essential raw materials in a variety of industrial processes. Some examples of basic chemical products include:
- Oxygen (O2): Oxygen is a gas essential for life and is used in a wide range of industrial applications, from metallurgy to energy production and healthcare.
- Nitrogen (N2): Nitrogen is an inert gas used for space inerting, such as in food preservation, and in the chemical and pharmaceutical industries.
- Hydrogen (H2): Hydrogen is used in the production of ammonia, hydrogenation of oils and fats, and as fuel in fuel cells.
- Chlorine (Cl2): Chlorine is a chemical element used in the production of chlorinated chemicals such as PVC and as a disinfectant in water treatment.
- Sodium (Na): Metallic sodium is used in organic synthesis, in the production of organic compounds such as metallic sodium and Grignard reagents.
- Potassium (K): Potassium is used in the production of fertilizers and is an essential element for plants.
- Calcium (Ca): Calcium is used in the production of construction chemicals such as cement, and in metallurgy.
- Sulfur (S): Sulfur is used in the production of sulfuric acid and in the vulcanization of rubber.
- Phosphorus (P): Phosphorus is used in the production of fertilizers, in the chemical industry, and in match manufacturing.
These basic chemical products are essential in numerous industrial processes and are generally obtained from natural sources or through specific chemical processes. They can also be used as reagents in various chemical reactions for the synthesis of more complex compounds. Their availability and production are crucial for many industries and sectors of society.